What is Pott’s Disease/Spinal Tuberculosis?
Overview
Spinal
tuberculosis or tuberculosis
spondylitis also known as Pott’s
disease is a spinal
infection caused by tuberculosis.
Symptoms of
spinal tuberculosis are kyphotic deformity, osteomyelitis, and spinal mechanical
instability.
Diagnosis is
made with CT-guided biopsy test for microscopic examination of acid-fast
bacilli and this microscopic examination is called Acid-fast staining.
Treatment is generally, practiced with formulated based on the with or without neurological involvement. However, with complicated TB spine patients, surgical invention is required with the addition of chemotherapy.
Tuberculosis and Pott’s disease/spinal
tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an exceedingly infectious
disease, especially in immuno-suppressed populations caused by the
bacterium, Mycobacterium tuberculosis which initially infects
the lungs. Still, in some cases, it can spread to other parts of the body. When
tuberculosis spreads, it’s referred t as extra-pulmonary tuberculosis (EPTB).
Joints and bones tuberculosis is one form
of EPTB.
Tuberculosis is the 13th primary cause of death worldwide and it is the second main infectious cause of death, after COVID-19. Most common in developing countries but increasing numbers of reported cases in developed countries as well.
Epidemiology
According to the CDC (Centers of Disease Control and Prevention) in 2020, more than 7,000 cases were reported in the United States.
Unfortunately, the cases of spinal tuberculosis (as with the other form of TB) are arising due to the new multiple drug-resistant strains.
WHO (The World Health Organization) about 1.5 million people died from this disease in 2020. Whereas, 10.4 million new cases of tuberculosis were reported in 2016, among which 46.5 % of cases were reported alone from the South East Asia region. India contributed 23% of the worldwide tuberculosis load.
Osteomyelitis or Discitis usually impacts the lower thoracic and upper lumber levels of the spine, comprising just about 50% of musculoskeletal TB.
Etiology
- Pronged exposure to infected patients
- Overcrowding
- Malnutrition
- Immuno-deficiencies (due to HIV, alcohol, drugs)
- Lower socio-economic situations
- Poverty
Symptoms
The symptoms or clinical presentation of spinal TB are inconsistent. The signs depend upon the- The severity of the disease
- Duration of illness
- Location of lesion
Pott’s disease or Spinal TB may develop when the air is contaminated with the TB-causing bacteria, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and the person breath into the lungs. This infection can spread from the lung to the spine through the blood called hematogenous. A person who has an active TB infection can infect the air with aerosol droplets, by speaking, spitting, coughing, sneezing, etc. Each sneeze can spread approximately 40,000 aerosol droplets, and only a single droplet can spread the infection.
Some common risk factors for Tuberculosis are
The presence of related complications includes neurological deficit and deformity.
Read also
Rhomboid pain, causes, symptoms, treatment
How to manage diabetes in work place
Constitutional symptoms
Genuine or constitutional symptoms include
- Loss of appetite
- Significant weight loss
- Fever
- Malaise/fatigue
- Night sweats
Symptoms of uncomplicated spinal tuberculosis
In uncomplicated spinal infection patients generally feel back pain, and this back pain can be related to the active disease itself (secondary to inflammation), instability, and bone destruction. Rest pain is pathognomonic and rarely, radicular pain may be the main spinal tuberculosis symptoms.
Symptoms of complicated spinal tuberculosis
In complicated spinal tuberculosis patients may present with instability, deformity, and neurologic deficit (present in 10-47% of patients).
Cold abscess
These abscesses characteristically do not have all the inflammatory noticeable signs that are generally obvious in abscesses.
Deformity
Unsettled with the greater involvement of the anterior spinal column in tuberculosis, the spinal column gradually develops a kyphosis, especially in the thoracic and thoracolumbar spine.
Neurological deficit
A neurological deficit may arise either at the active stage of the disease resulting in compression from an abscess, spinal stability, sequestrum, or inflammatory tissue, or it may happen during the healed stage typically secondary to mechanical traction spinal defect.
Spinal tuberculosis in kids
Children are more prone to developing severe deformity progression due to increased flexibility of the spine and immaturity in kids. These worsening deformities may also occur after the disease has completely healed, so follow-up is crucial until skeletal maturity.
Read also
Psyllium husk powder, how to use, benefits
Diagnosis
Following tests are generally run for the diagnosis of
Tuberculosis
Sputum culture
- X-rays
- Blood culture
- Mantoux tuberculin skin test
- Tissue biopsy (to check the possibility of cancer)
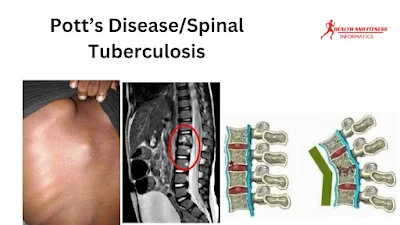
CT Scan; A computerized tomography (CT) scan is a medical technique to capture detailed internal images of the body.
This scan provides much better bony detail of irregular lytic
lesions, disk collapse, disruption of bone circumference, and sclerosis than
X-Rays. This scan discloses before-time lesions and much effective for defining
the calcification of soft tissue abscess that is common Tuberculosis.
MRI; Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique in which a strong magnetic field, radio waves, and magnetic field gradient are used to create images of the organ of the body. MRI is also considered the most effective imaging study for indicating neural compression. MRI is a valuable way of diagnosing certain diseases that a CT scan can’t detect.
Importance of MRI in diagnosis
1. MRI is the decisive factor for evaluating osteomyelitis and
disk-space infection of the spine.
2. MRI is also known as the most effective imaging study for
indicating neural compression.
3. This diagnostic technique is also most effective for demonstrating
the spread of tuberculous debris under the posterior and anterior longitudinal
ligament and the extension of disease into soft tissue.
4. MRI results are useful to distinguish tuberculous spondylitis from
pyogenic spondylitis comprise smooth and thin enhancement of the abscess wall
and precise paraspinal abnormal signal, while irregular and thick enhancement
of abscess wall and ill-defined paraspinal abnormal marks recommend pyogenic
spondylitis. Consequently, distinguish-enhancement MRI showed to be crucial in the differentiation of these two types of spondylitis.
Biopsy: is a medical procedure to remove a sample of cells or
pieces of tissue from the body so that can be tested in a laboratory.
For the diagnosis of spinal tuberculosis percutaneous CT-guided
biopsy of bone and lesions can be used to get tissue samples. The biopsy is a
safe medical procedure that also allows therapeutic drainage of large
paraspinal abscesses.
PCR test: Polymerase chain reaction
(PCR) technique magnify species-specific DNA sequences, that are able to
rapidly identify and diagnose many strains of mycobacterium without the need
for prolonged culture.
PCR tests have also been
used in DNA sequences associated with drug resistance.
ESR: Erythrocytes sedimentation rate
(ESR) is done to measure how quickly red blood cells settled in the bottom of
the test tube because infection or inflammation may lead to protein in the
blood, which can facilitate red blood cells settling down faster.
In patients with bone TB or Pott’s disease usually, ESR is
elevated but may be normal in up to 25%.
CBC: Complete Blood Count (CBC)
blood test is done to evaluate a person’s overall health and detect a wide
range of disorders including anemia. In males and females, there are different
normal ranges.
Patients with spinal TB usually have low hemoglobin and relative
lymphocytosis.
PPD: Purified protein derivative of tuberculin (ppd) is a skin test
that determined if the patient has a serious TB infection.
Ppd test is usually 80% positive for spinal TB.
Read
more about 6-week
Ozempic weight loss before and after
Treatment
The
stronghold of treatment in spinal tuberculosis is chemotherapy, in which
anti-tubercular treatment follows. Tubercle bacilli (Mycobacterium tuberculosis
bacilli) may be present as extracellular or intracellular forms or rapidly
multiply forms or as dormant. In order to reduce the instance of drug
resistance and to attack the bacilli in various stages or forms, multi-drug
treatment is very important.
It is
very important to classify spinal tuberculosis as an uncomplicated and
complicated disease, based on its appearance.
- Uncomplicated spinal tuberculosis is basically a
medical disease.
- Complicated tuberculosis patients need surgical intrusion
with the combination of chemotherapy
The first line of treatment for
spinal TB or pott’s disease is the surgical removal of the tubercular
infection. Administration of anti-tubercular medications (use of antibiotic) is
done before and after the surgical procedure. This procedure is pursued by the
surgical reconstruction o the spine.
The
treatment protocol is prepared based on the absence or presence of neurological
involvement. Usually, pharmacotherapy is preferred over surgery in case of
neurological involvement. Pyrazinamide, Rifampicin, Isoniazid, and Etahmbutol
drugs use as an anti-tubercular medications in pharmacotherapy.
With a
safe and better response, surgery done during the active stage of
infection/disease is much safer.
Physical therapy management
Patients
with spinal tuberculosis or pott’s disease often undergo spinal compression or
spinal fusion surgeries to correct their structural deformity and prevent
further neurological complications. There are no recognized guidelines that
dictate the treatments that will defer positive effects in such patients.
However, treatment schedules should deal with each patient individually, focal
pointing to any injury functional restrictions, and/or disabilities with which
they present.
Disease in children, the need for regular
follow-up until skeletal maturity requires to be obviously communicated to the
blood relations and the chance of progression of deformity still years after
healing of the disease.
Read more
about What
is hyperthyroidism or overactive thyroid
1.
2. MRI is also known as the most effective imaging study for
indicating neural compression.
3. This diagnostic technique is also most effective for demonstrating
the spread of tuberculous debris under the posterior and anterior longitudinal
ligament and the extension of disease into soft tissue.
4. MRI results are useful to distinguish tuberculous spondylitis from
pyogenic spondylitis comprise smooth and thin enhancement of the abscess wall
and precise paraspinal abnormal signal, while irregular and thick enhancement
of abscess wall and ill-defined paraspinal abnormal marks recommend pyogenic
spondylitis. Consequently, distinguish-enhancement MRI showed to be crucial in the differentiation of these two types of spondylitis.
For the diagnosis of spinal tuberculosis percutaneous CT-guided biopsy of bone and lesions can be used to get tissue samples. The biopsy is a safe medical procedure that also allows therapeutic drainage of large paraspinal abscesses.
PCR test: Polymerase chain reaction
(PCR) technique magnify species-specific DNA sequences, that are able to
rapidly identify and diagnose many strains of mycobacterium without the need
for prolonged culture.
ESR: Erythrocytes sedimentation rate
(ESR) is done to measure how quickly red blood cells settled in the bottom of
the test tube because infection or inflammation may lead to protein in the
blood, which can facilitate red blood cells settling down faster.
In patients with bone TB or Pott’s disease usually, ESR is elevated but may be normal in up to 25%.
CBC: Complete Blood Count (CBC)
blood test is done to evaluate a person’s overall health and detect a wide
range of disorders including anemia. In males and females, there are different
normal ranges.
Patients with spinal TB usually have low hemoglobin and relative
lymphocytosis.
Ppd test is usually 80% positive for spinal TB.
Treatment
The stronghold of treatment in spinal tuberculosis is chemotherapy, in which anti-tubercular treatment follows. Tubercle bacilli (Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacilli) may be present as extracellular or intracellular forms or rapidly multiply forms or as dormant. In order to reduce the instance of drug resistance and to attack the bacilli in various stages or forms, multi-drug treatment is very important.
It is very important to classify spinal tuberculosis as an uncomplicated and complicated disease, based on its appearance.
- Uncomplicated spinal tuberculosis is basically a medical disease.
- Complicated tuberculosis patients need surgical intrusion with the combination of chemotherapy
The first line of treatment for spinal TB or pott’s disease is the surgical removal of the tubercular infection. Administration of anti-tubercular medications (use of antibiotic) is done before and after the surgical procedure. This procedure is pursued by the surgical reconstruction o the spine.
The treatment protocol is prepared based on the absence or presence of neurological involvement. Usually, pharmacotherapy is preferred over surgery in case of neurological involvement. Pyrazinamide, Rifampicin, Isoniazid, and Etahmbutol drugs use as an anti-tubercular medications in pharmacotherapy.
With a safe and better response, surgery done during the active stage of infection/disease is much safer.
Physical therapy management
Patients with spinal tuberculosis or pott’s disease often undergo spinal compression or spinal fusion surgeries to correct their structural deformity and prevent further neurological complications. There are no recognized guidelines that dictate the treatments that will defer positive effects in such patients. However, treatment schedules should deal with each patient individually, focal pointing to any injury functional restrictions, and/or disabilities with which they present.
Disease in children, the need for regular follow-up until skeletal maturity requires to be obviously communicated to the blood relations and the chance of progression of deformity still years after healing of the disease.
Read more about What is hyperthyroidism or overactive thyroid
Physical therapy management post-spinal decompression surgery
1.
Exercise and strengthening
2. Spinal Stabilization Exercise
3. Back School
4. Maitland
When evaluated with self-management spinal
stabilization exercise and the other physical therapy treatments, self-spinal
stabilization exercises were found to turn out considerably more positive
ratings in worldwide outcomes. Disability and pain, however, did not show
considerable improvement when measured up to the other two treatment options.
1.
2. Spinal Stabilization Exercise
3. Back School
4. Maitland




.jpg)
Post a Comment